Why is it Important to Know About Radon?
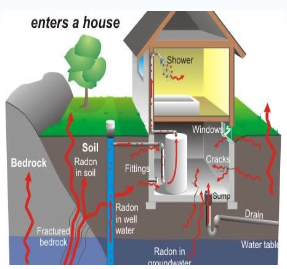
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas found in soil, rock, and water throughout the U.S. It is commonly found in New England. The primary concern about indoor radon gas is the increased risk of lung cancer from breathing radon and its byproducts. The magnitude of the risk depends on the radon concentration in the air you breathe and how long you are breathing it. Testing for radon in the air you breathe should be a high priority and the first step for anyone concerned about radon gas. The U.S. Surgeon General, U.S. EPA, AARST, and the American Lung Association recommend that all homes be tested for radon gas.
Our radon air tests are performed with Sun Nuclear CRM 1027 continuous monitoring systems. These machines take hourly readings for 48 hours and calculate the EPA protocol average. They have internal motion sensors that detect and report any movement during testing.
Do You Need a Home Inspection Services?
If so, contact the professionals at About the House at 603-552-5959.

